CORS Setup
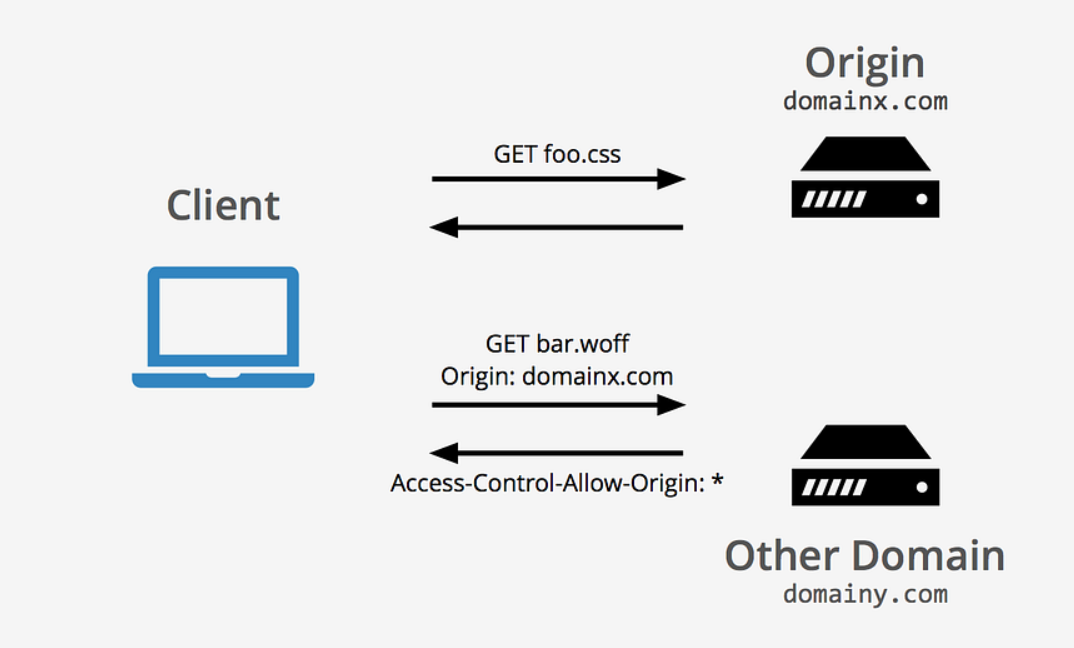
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a security feature implemented by web browsers to prevent unauthorized domains from accessing resources on a server. Configuring CORS properly is essential for enabling communication between a frontend and a backend hosted on different origins.
Why Configure CORS?
By default, web browsers block requests made from a different domain than the server's. This restriction can interfere with the development of web applications where the frontend and backend run on different ports or domains. CORS configuration in a Spring Boot application enables secure cross-origin requests.
Global CORS Fix Configuration
To set up CORS globally in a Spring Boot application, a configuration class can be created. Below is an example implementation for RaiseHub.
Code Example
com/fontys/crowdfund/config/WebConfig.java
package com.fontys.crowdfund.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer corsConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**") // Allow all paths
.allowedOrigins("http://localhost:3000") // Allow only frontend origin
.allowedMethods("GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE") // Allow common HTTP methods
.allowedHeaders("*") // Allow all headers
.allowCredentials(true); // Allow credentials such as cookies
}
};
}
}
Breakdown of the Configuration
@ConfigurationAnnotation: Marks this class as a configuration class.@BeanAnnotation: Registers a bean that provides CORS configuration.addCorsMappingsMethod: Configures allowed paths, origins, methods, headers, and credentials.
Explanation of Key Settings
- Allowed Paths (
addMapping("/**")): This setting allows CORS requests on all API endpoints. - Allowed Origins (
allowedOrigins("http://localhost:3000")): Restricts requests to the specified origin (frontend). - Allowed Methods (
allowedMethods(...)): Defines supported HTTP methods. - Allowed Headers (
allowedHeaders("*")): Permits all headers. - Allow Credentials (
allowCredentials(true)): Enables sharing of cookies, authentication headers, and other credentials.
Best Practices
- Use Environment Variables: Avoid hardcoding origins in production.
- Limit Origins in Production: Allow only trusted origins to access the API. (This is specially important)
- Secure Headers and Methods: Restrict methods and headers to minimize the application's attack surface.